
In accordance with the planning of China Meteorological Administration (CMA), by the end of this December, smart grid forecast operation will be formally initiated. The spatial resolution of this network reaches 5km×5km, enabling 10-day weather forecast every 3 hour. The public can get their hands on refined location-based meteorological service at any time, signifying that weather forecast can make the transition from site forecast to grid forecast.
Technical features of smart grid forecast
Smart grid forecast mainly encompasses two kinds of technologies and two pillars.
The first technology is a refined grid forecast technology integrating subjective and objective factors. This technology combines forecasters' expertise in predicting key disastrous weather with objective NWP dynamic interpretation method, bringing about more accurate and refined forecast. The second technology is underpinned by multi-source scene analysis which conducts repeated forecast. It is also based on real-time error between the true situation and the forecast and establishes an updated model of temperature, precipitation, and wind on an hourly basis, which elevates the efficacy of the service.
The first pillar is numerical weather prediction (NWP) cloud. Over the long haul, meteorological operation is confronted with the issue of transmitting a multitude of NWP data. The second pillar is CIMISS platform, which facilitates the smooth operation of data flow and provides support for the information distribution and sharing of smart grid forecast.
Production procedures of smart grid forecast
The national-level meteorological departments will first release national smart grid forecast product and distribute it to the entire country. Provincial meteorological departments will make their smart grid forecasts based on their own predictions and methods and refer to national forecast at the same time. Then they will share the final versions with national meteorological departments. Therefore, at the national level, the two kinds of forecast will be rapidly integrated. Different provincial departments will release smart grid forecasts. 31 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) possess their respective forecasting products, constituting constantly updated version of the smart grid forecast network.
The national version takes into account the discrepancies existed in the entire nation, and formulates the forecast with 5km×5km spatial resolution. While different provincial meteorological departments can make prediction products with higher resolution based on their technical capacity and actual conditions.

National-level smart grid meteorological forecasting operation Provided by Xue Feng
Smart grid forecast has grabbed the attention of the public in recent years. But its technical development actually predated this phenomenon.
Weather forecast is in the midst of the transition from qualitative forecast, descriptive forecast to digitalized forecast and grid forecast. For instance, prior urban weather forecast only contained contents such as weather phenomena of over 2400 cities and towns, with forecast of high temperature, low temperature, wind speed, wind direction. The temporal and spatial accuracy was not high. In 2012, National Meteorological Centre (NMC) launched a new forecasting product, namely refined forecast of big cities. This product will conduct forecast of provincial capitals and municipalities with independent planning status at 6-hour intervals. However, this product was not refined enough to cater to the demand of all manner of sectors and the general public.
The demand fosters the development of operation. Around 2010, the concept of grid forecast was introduced into the refined forecast operation of China.
Compared with the previous fixed site forecast, grid forecast is more refined and targeted from the spatial angle. At present, some provinces can realize minute scale weather forecast. A dozen provinces can realize 3km resolution, 2.5km resolution, and even more refined forecast.
Refined grid forecast is also manifested in higher frequency of updating and distribution on a daily basis. Previously, weather forecast within one day only involved one kind of weather phenomenon. Right now, it can realize 10-day forecast every 3 hour at the national level. The public can have a clear picture of basic meteorological factors such as temperature, precipitation, and wind.
Meteorological departments also divide sea area of China into several 10km×10km grids, and conduct refined forecast of sea visibility and gale at sea.
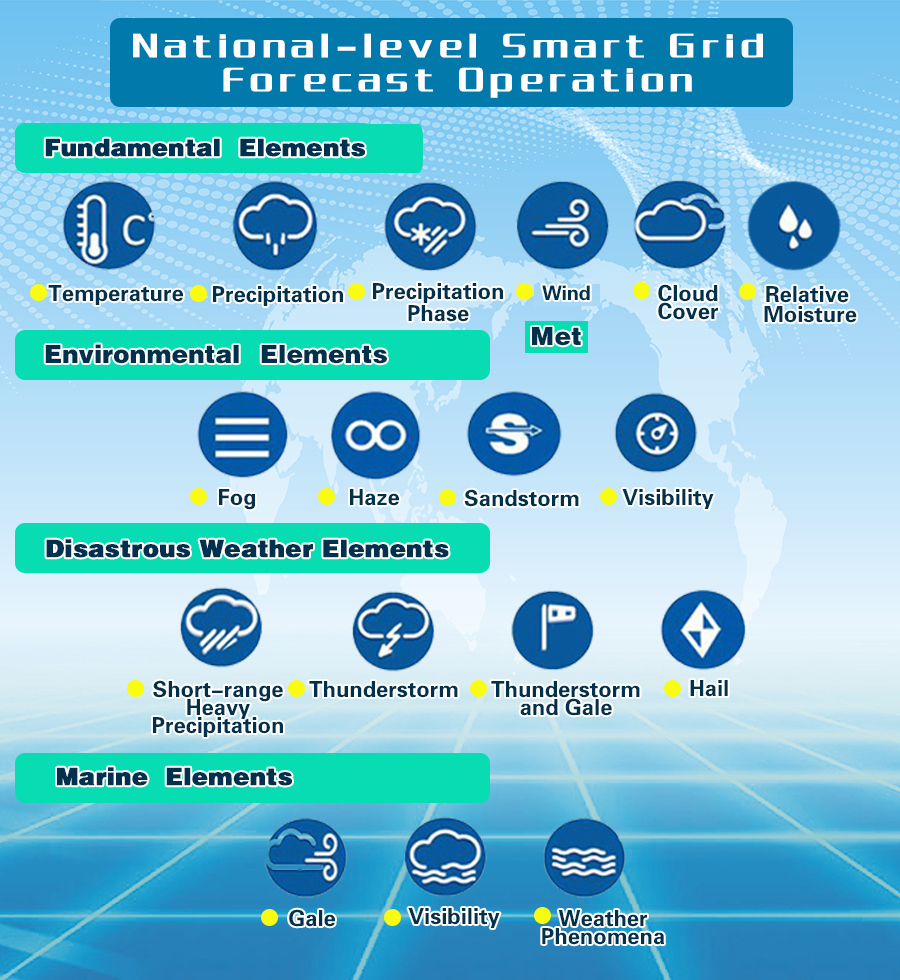
18 meteorological elements, 4 categories
Currently, land and ocean forecasting products have encompassed 4 categories and 18 meteorological elements.
This forecast grid with an increasing higher temporal and spatial resolution has become the most significant forecasting product. In the future, forecasting products from meteorological departments will be derived from this network at any time.
As grid forecast evolves, contents of products will become more comprehensive with a mounting data volume. Different meteorological departments rely on refined grid forecast, integrate service approaches based on location, website and mobile terminal, and provide the most accessible and targeted services and products for the public. Some provinces also release grid forecast or even provide hourly-updated weather forecast for people planning a trip.
One of the core features of smart grid forecast is smart-based.
NWP and ensemble forecast embody the most cutting-edge smart-based meteorological technological achievements. High resolution smart grid forecast should be underpinned by high resolution regional NWP model. Currently, China has 4 sets of operationalized high resolution models, namely GRAPES, and models developed by Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangdong regional meteorological center respectively.
CMA has established a NWP cloud in Shanghai. Meteorological departments in the entire country can conduct rapid sharing of high resolution NWP modeling products through the cloud terminal. Provincial departments will execute data handling, diagnosis and analysis, interpretation and application, interaction and correction of the modeling, and formulate provincial-level forecasting products.
In the future, meteorological departments will integrate physical mechanism and NWP big data mining.
Meteorology is a complex system, which is affected by many elements such as precipitation, vapor, and moisture.
Forecasters excel in grasping key weather conditions. In the preliminary stage of smart forecast, years’ experience in prediction enables forecasters to facilitate machines and models. As modeling and smart-based technology evolves, room for manual correction will narrow. Some forecasters will engage in technological development while some of them will turn to meteorological services for key weather processes.
At present, related CMA teams have joined hands with institutions like Tsinghua University and Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) in artificial intelligence technology research and development; National-level meteorological departments have also organized smart forecasting service prototype team; veteran chief forecasters, young RD-oriented forecasters, and IT engineers also constitute big data and smart forecast teams. All these efforts will pronouncedly advance smart grid forecast development and lend a hand to meteorological forecasting services.

Future Smart Forecasting System Provided by Xue Feng
From June 21 to June 24 in 2017, the average rainfall amounted to 92 mm in entire Beijing. On the evening of June 21, rumor was rampant online about the emergence of the so-called heaviest rain. On the deep night of June 22, rainstorm finally occurred.
Weather forecast on this occasion is accurate, but it was not in full compliance with the demand of the general public. How to comply with their demand is what smart grid forecast should grapple with. The initial objective of smart grid forecast lies in dividing the entire country into 5km×5km grid. On this foundation, forecast will be updated at 1-hour interval. In case of major weather process, the frequency will be accelerated.
From the perspective of meteorological science, at the same technological level, when temporal and spatial resolution increases, the accuracy of weather forecast, in general, will be lower. However, meteorological departments should guarantee that the accuracy of smart grid forecast can outpace that of site forecast during the trial operation stage.
Frankly speaking, meteorological departments should transform traditional forecast and formulate grid forecast with high temporal and spatial resolution, even though it may incline to diminish the prediction accuracy. This kind of forecast is service-based demand.
Smart grid forecast can provide accurate meteorological services based on IP and mobile phone location. Prediction services encompass factors such as rainfall, wind, temperature, moisture, cloud cover, and visibility.
Grid forecast will be refined quantitative digitalized forecast, instrumental in conducting disastrous weather impact forecast. Based on refined smart grid, forecasters can conduct more accurate forecast of disastrous weather impact in case of geological hazards, rainstorm, flooding, heat wave and drought.
Besides, based on refined grid forecast, related sectors like agriculture, transportation or tourism will profit from more refined meteorological services.
As meteorological science and technology burgeons, grid forecast will become more refined. Last year, CMA started to develop global grid forecast. In this manner, even outside China, meteorological services will come in handy.
Editor: Liu Shuqiao