Some sophisticated technologies in this year’s flood season
Source: China Meteorological News Press
Date: 2020/11/05
In 2020, we have witnessed an eventful flood season, which has been exposed to river basin type flooding in a handful of rivers and several typhoons repeatedly slamming Northeast China.During this process, meteorological science and technology has played an instrumental role.They have fully given play to their role in providing support and serving as cutting-edge tools in comprehensive disaster preparedness. Monitoring Gaofen satellite has harnessed satellite-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) to penetrate the cloud and fog monitoring the main body and water basin area change of the Poyang Lake. During this year’s flood season, flood conditions in the Yangtze River Basin were urgent, with Poyang Lake experiencing soaring water levels. Due to the blocking of cloud and fog over the optical satellite, it could not carry out comprehensive and effective observations of the ground surface. SAR is capable of penetrating cloud and fog and carrying out all-weather monitoring, which can permeate the cloud layer to directly observe the flood disaster effects in the targeted area and carry out meter-scale resolution observation. Since the mid-July, Huaihe River Basin was subjected to heavy rain. Wangjiaba Dam discharged the flood and the flood water storage area was activated. National Satellite Meteorological Center (NSMC) of China Meteorological Administration (CMA) obtained first-hand multi-source satellite observation data from Fengyun meteorological satellites and Gaofen-3 satellite, continuously monitored Mengwa flood storage area in Huaihe River and neighboring water body changes, and provided support for disaster mitigation as well as government decision making.
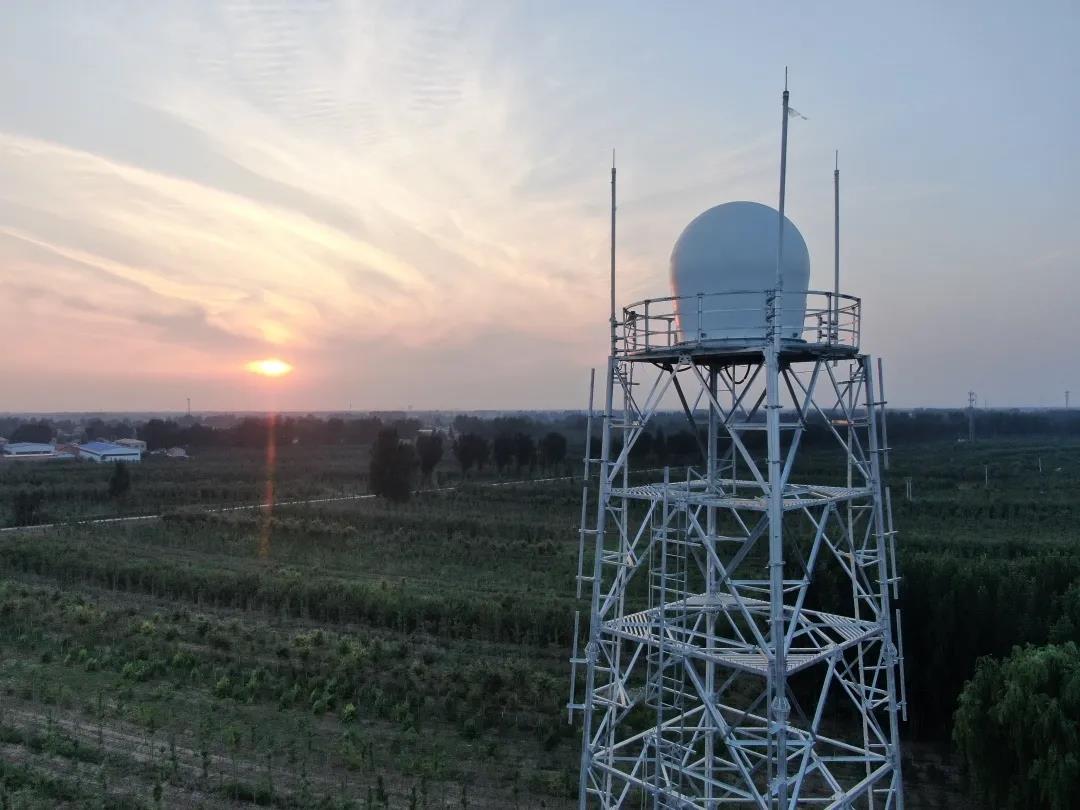
X-band phased array weather radar installed in Xiong’an New Area X-band phased array weather radar installed in Xiong’an New Area has the advantages of high speed, high resolution, ultra-low data time difference, full coverage detection of the wind field and intensity field, and others. During the prediction and services of heavy rain from July to August in 2020, the radar has identified newborn convection cell 4-6 minutes in advance, and bought more time for forecasters to distribute severe weather early warning. The wind field data has also provided potent support for the accurate identification of heavy rain. Through three-dimensional profiling products, the refined and complete three-dimensional structure of convection cell can be obtained. And forecasters can predict potential severe weather types according to the aforementioned information.
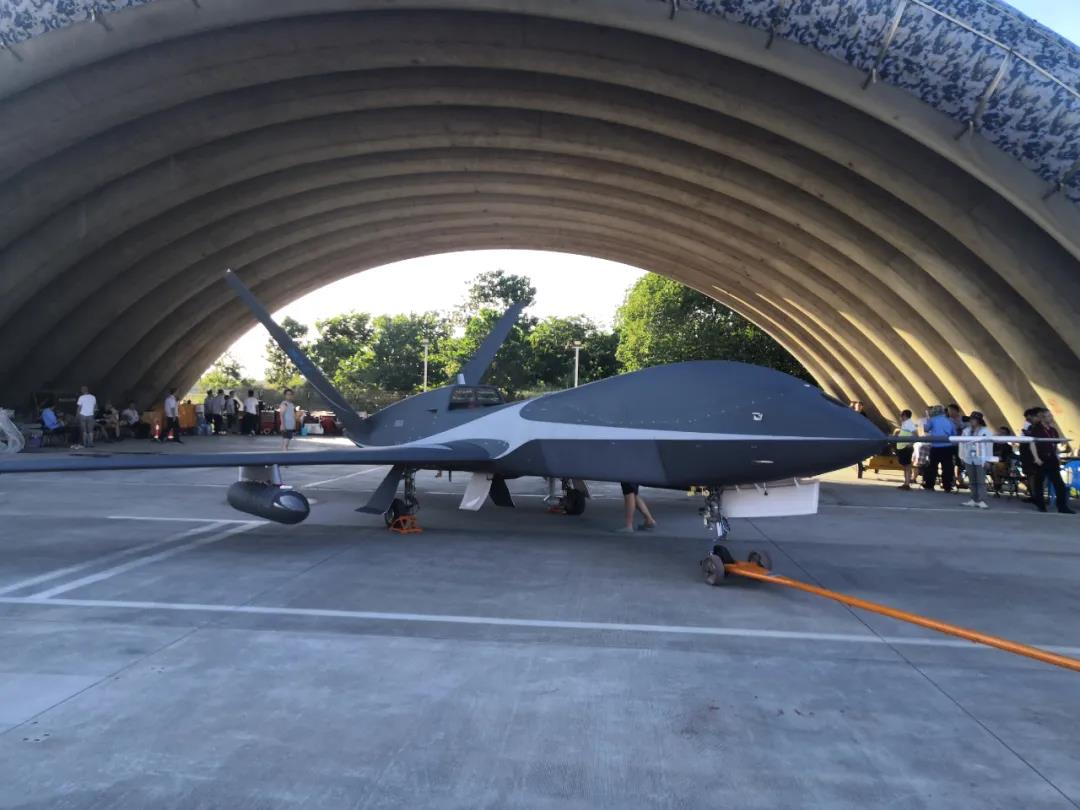
Upper air meteorological sounding drone On August 2, during the impact period of the third typhoon Sinlaku of 2020 on Hainan, an upper air meteorological sounding drone lifted off from Boao Airport and dropped down 30 sounding instruments. These instruments, together with millimeter band radars, carried out CT three-dimensional scanning of peripheral cloud systems of the typhoon. The data from this comprehensive sounding experiment has provided key reference basis for forecasters to determine the center location of typhoon Sinlaku. The drone and sounding payloads harnessed by the experiment are independently developed by China.
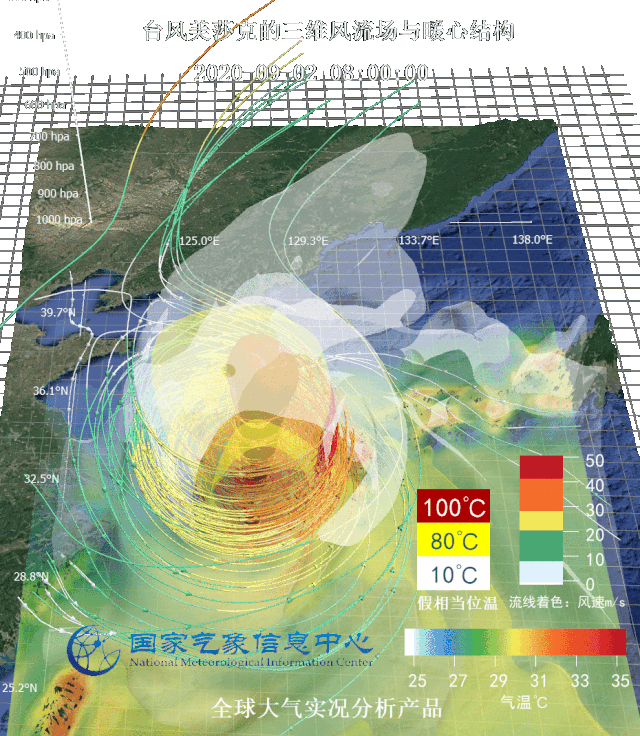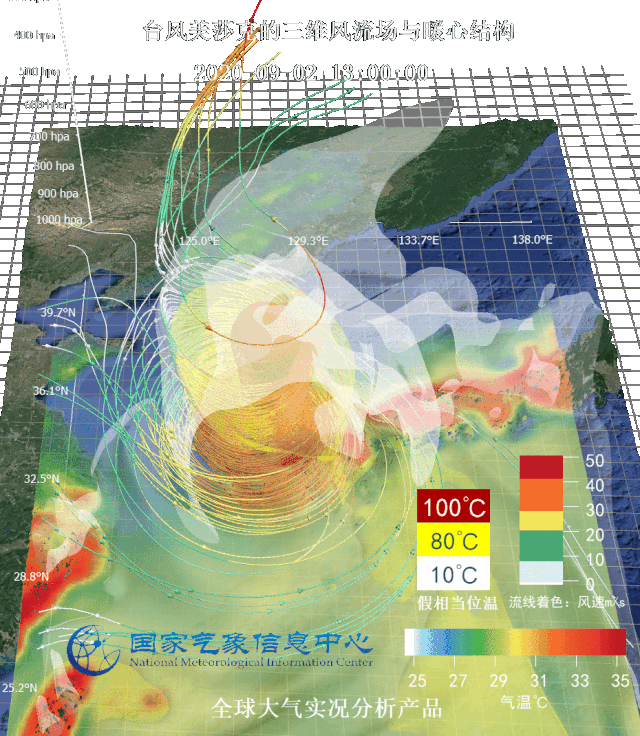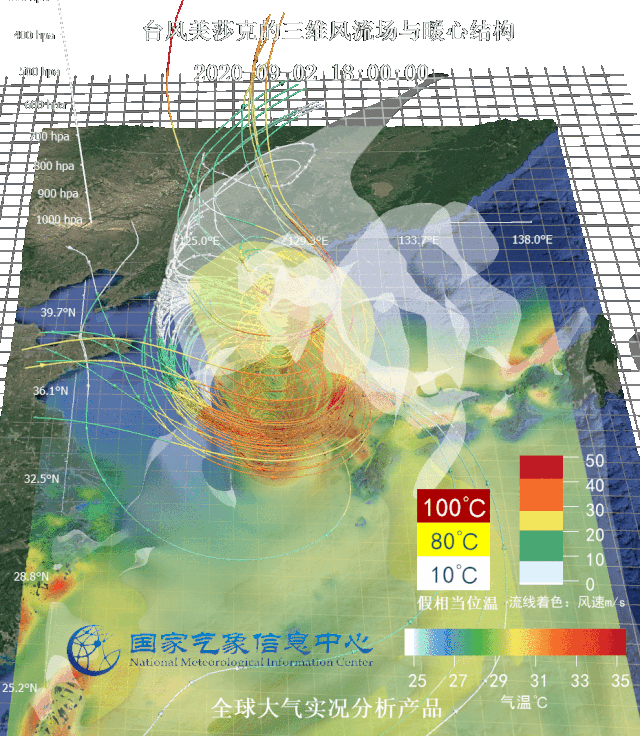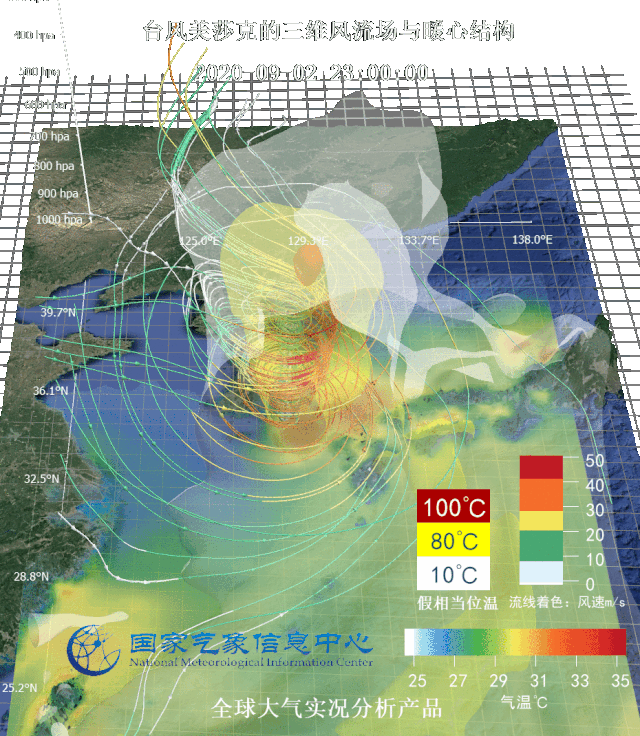
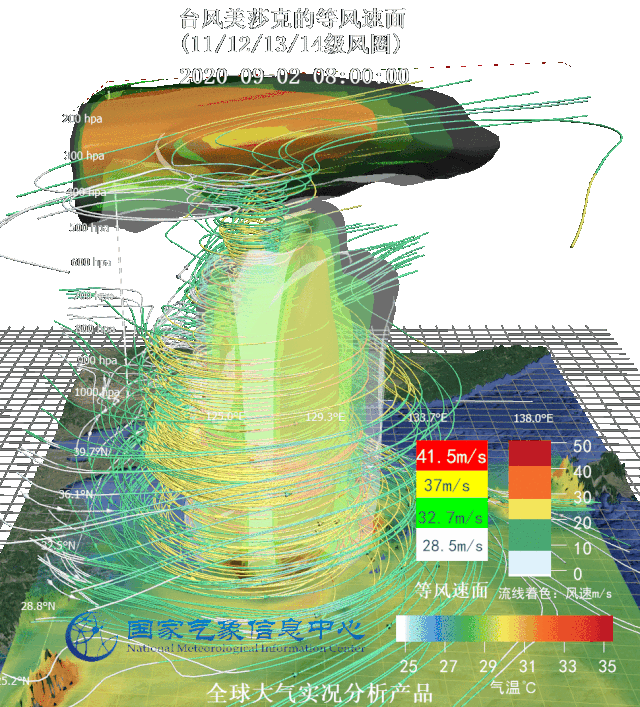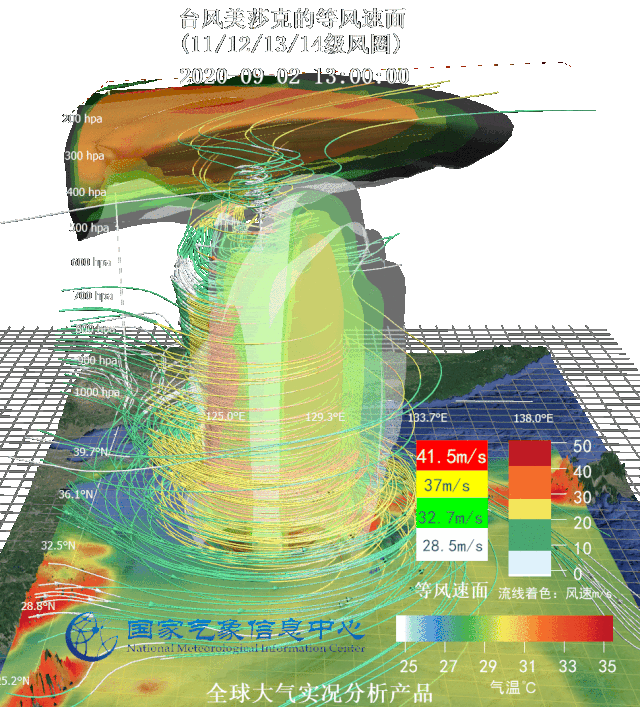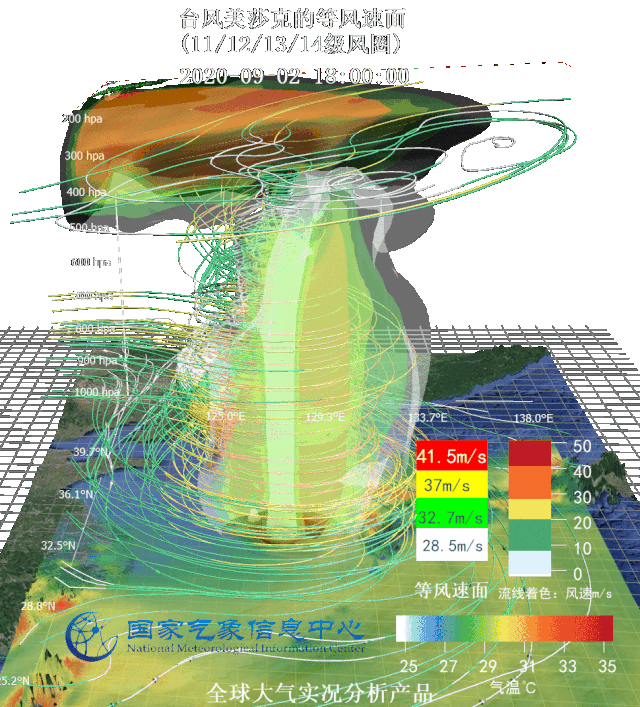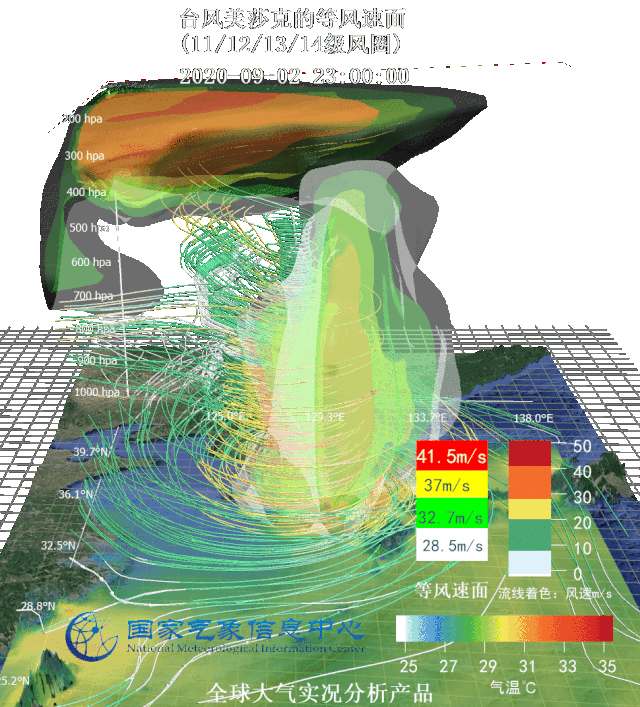
Three-dimensional wind flow field and warm center structure of typhoon Sinlaku (up) and equal wind velocity area image (down) Targeted at several typhoons affecting Northeast China in 2020, National Meteorological Information Center (NMIC) made three-dimensional motion graphs based on real-scene analysis data and multi-source integrated reanalysis data, observed typhoons from the perspective of data and dissected the internal structure of typhoons.
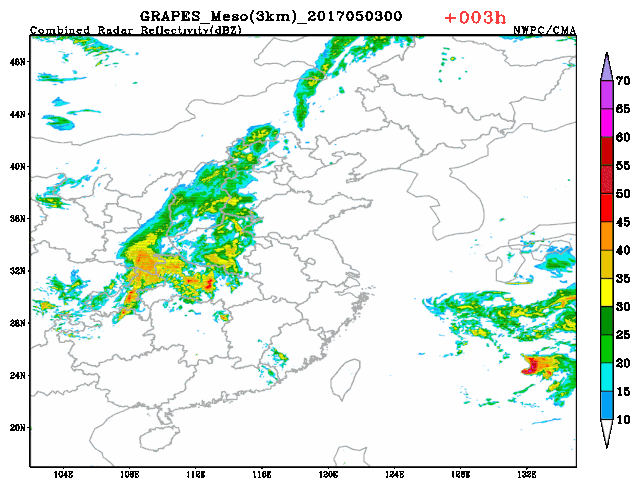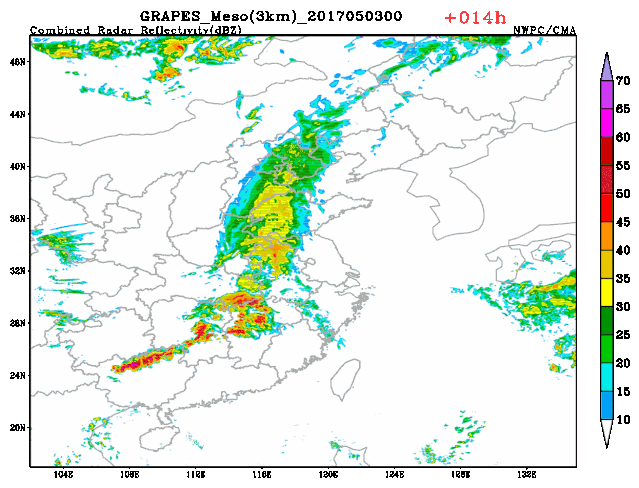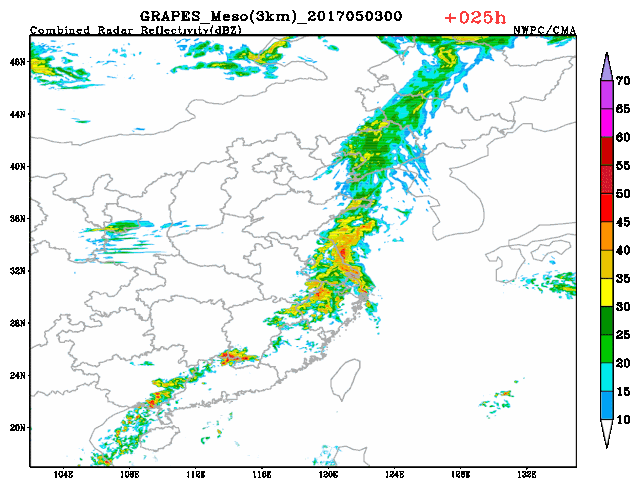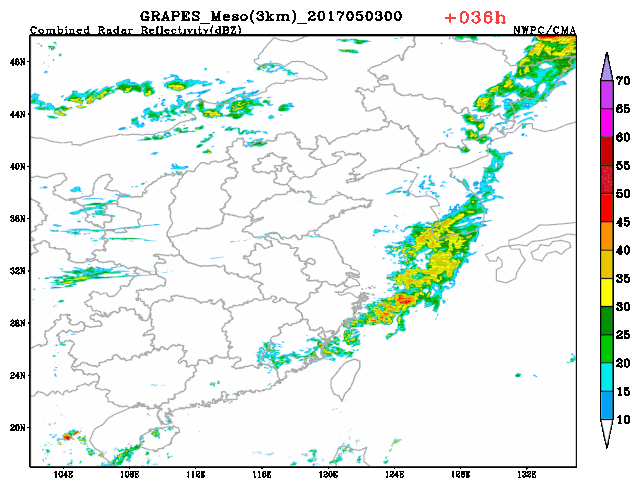
3-km regional GRAPES radar composite reflectivity fitting prediction The upgraded version of the GRAPES global assimilation prediction system and regional numerical weather prediction (NWP) system in 2020 have stood the test of many complex weather during the flood season. The upgraded GRAPES global assimilation prediction system has noticeably elevated the prediction capacity of stratosphere, and improved the medium and long term precipitation prediction level. The upgraded GRAPES regional numerical weather prediction (NWP) system has realized the 3-km resolution rapid cycle assimilation prediction at 3-hour interval at the national scale, which has further ramped up short range nowcasting capacity and met the demand of localized severe convective weather, in particular, severe and extreme weather events.
Smart meteorological service integrated operational platform in the Yangtze River Basin In the Yangtze River Basin which has experienced severe flood condition this year, the basin meteorological center has developed an integrated operational platform which has rolled a few functions into one such as hydro-meteorological information coordination and analysis, prediction service smart reminder, basin precipitation grid point correction, rapid integration of data product, and real-time feedback of forecast verification and assessment. It has played a notable application role. ServiceAI was harnessed to automatically make the short video of yellow warning of gale in Tianjin During this year’s flood season, CMA Public Meteorological Service Center joined hands with Baidu to develop and roll out AI early warning short video, harness AI technology to identify early warning information location, early warning category, and other core early warning information, and generate new type short videos rolling comprehensive map location information, defense guideline, and rotating broadcast. Automatic making of AI early warning smart videos only takes about 90 seconds. Over 1000 videos can be produced per day. This technology has been applied on about 3000 early warning baijiahao accounts, a Baidu social media, of national early warning information distribution institutions. It has not only saved manpower but also elevated the distribution effect of early warning information. From May to August, 106219 early warning short videos have been made.
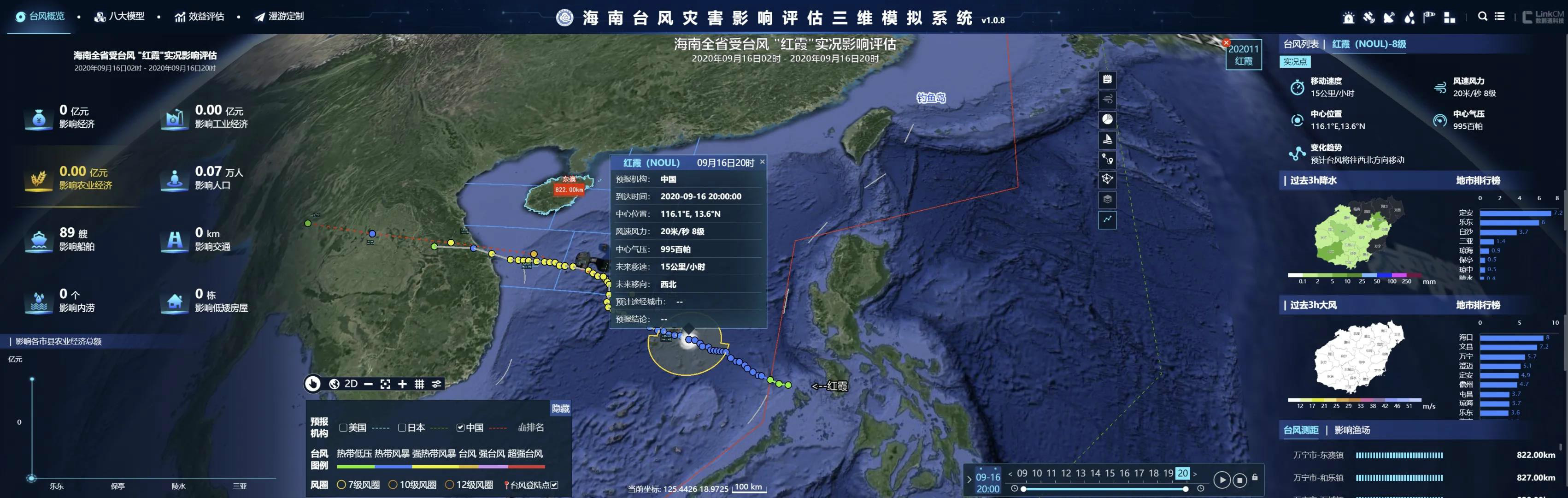
Three-dimensional modeling system of typhoon disaster effects in Hainan
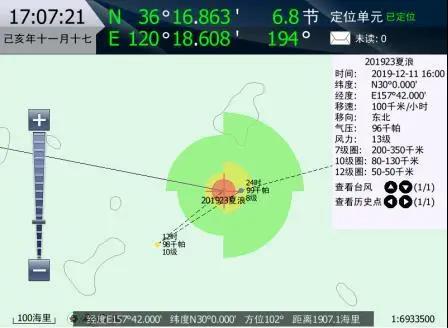
Fishers received meteorological information distributed by Beidou boat-borne terminal visible meteorological early warning service system In Hainan, three-dimensional modeling system of typhoon disaster effects was based on Beidou satellite boat locating data, combines prediction like wind speed and direction, sea wave, and sea current provided by meteorological and ocean departments, and carried out dynamic assessments of navigation risk scale of different types of boats in South China Sea. Hainan Provincial Meteorological Service applies myriad types of data processing algorithms, conducts digital processing of weather phenomena, surface topography, surface structures, and hazard inducing regions, harnesses three-dimensional virtual real scene technology to complete three-dimensional visible overlapping under the same space time, and realize the organic integration of three-dimensional modeling and disaster effect assessment. The Hainan Provincial Meteorological Service has developed refined Beidou boat-borne terminal visible meteorological early warning service system to provide real-time visible severe weather prediction and early warning for boats to help fishers timely judge the best route and timing to evade risks. For instance, the smart early warning service model developed by Hunan Provincial Service is based on telecommunication operators and meteorological big data, and harnessed technologies like geofence to accurately release early warning information geared to some disaster-hit areas.(Nov.5) Editor: Liu Shuqiao Previous issues
|